Glutamate — Zebrafish UCL
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Last updated 23 mai 2024
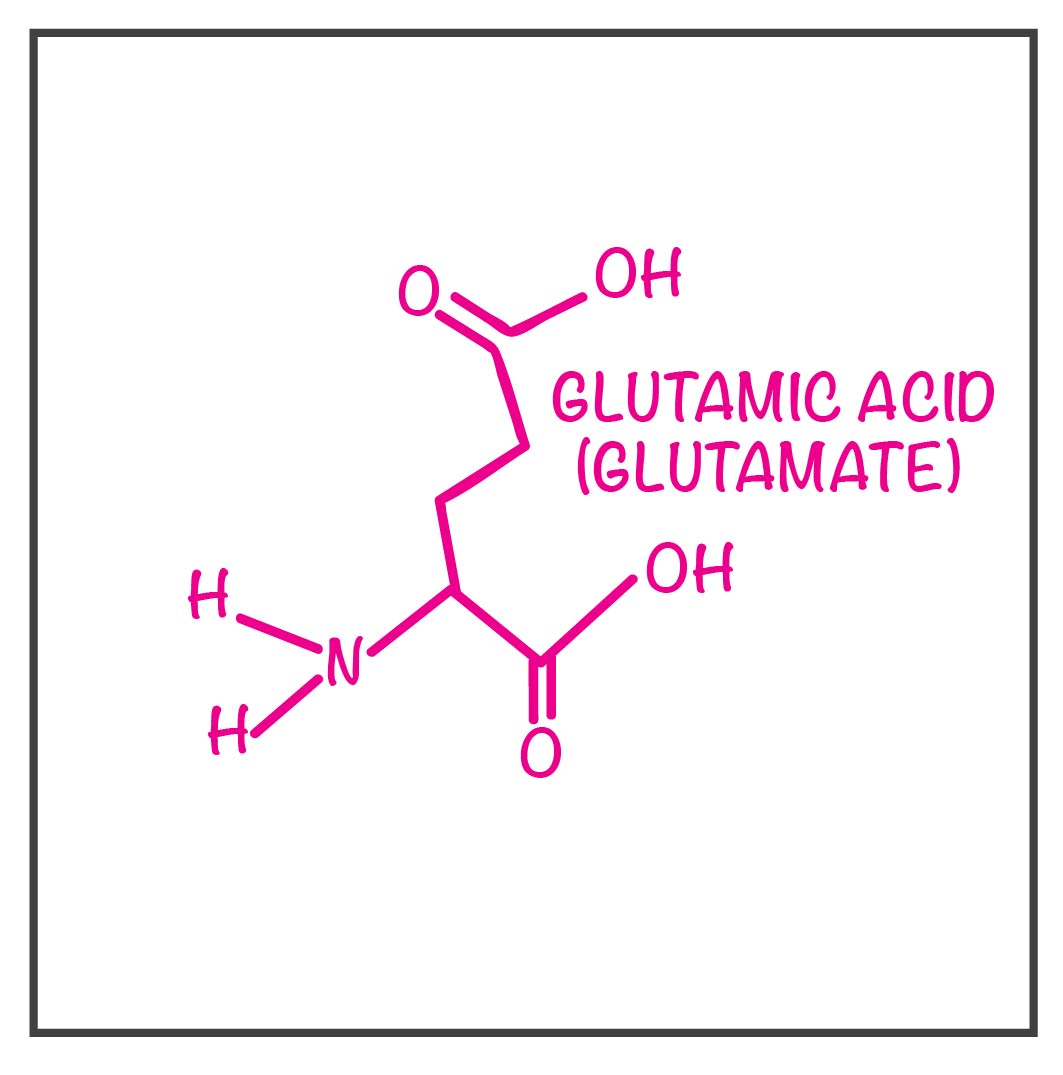
Glutamate is the anion of glutamic acid(an amino acid). It is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the nervous system of the zebrafish and other vertebrates. Post-synaptic transmission of glutamate is mediated by four types of glutamate receptors: NMDA receptors : ionotropic transme
Neurotransmitters — Neurotransmitters — Zebrafish UCL

Behavioural pharmacology predicts disrupted signalling pathways
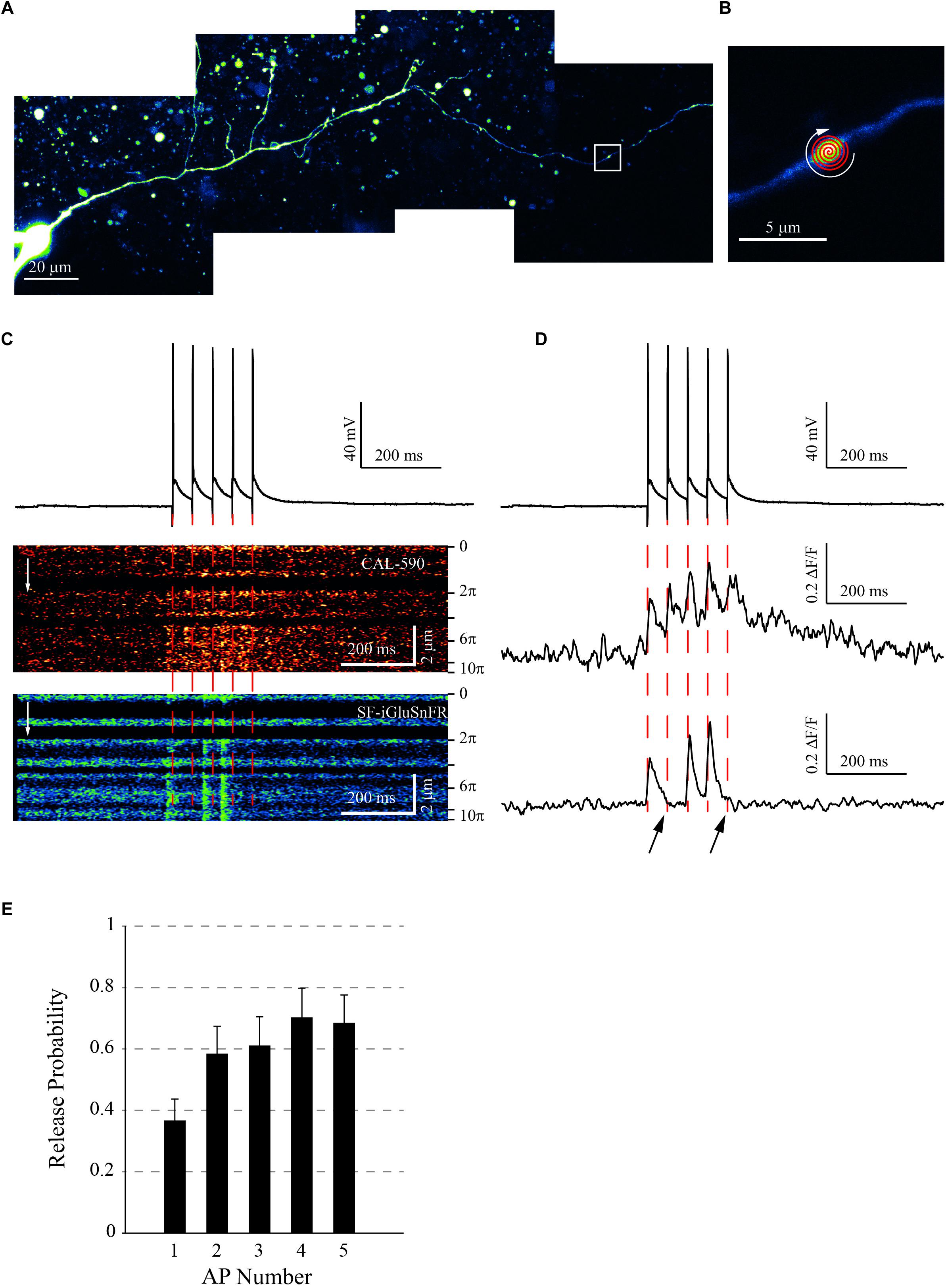
Frontiers Glutamate Imaging Reveals Multiple Sites of Stochastic

Behavioural pharmacology predicts disrupted signalling pathways
Glutamate — Zebrafish UCL
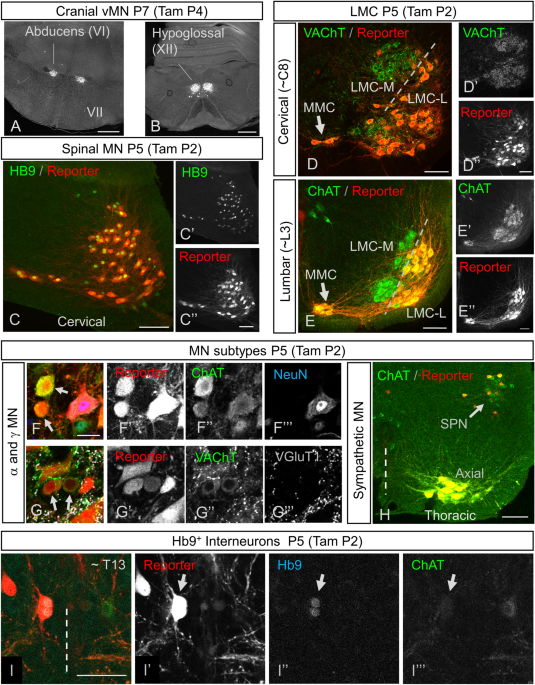
Elimination of glutamatergic transmission from Hb9 interneurons

Nitric Oxide Synthase Regulates Morphogenesis of Zebrafish Spinal
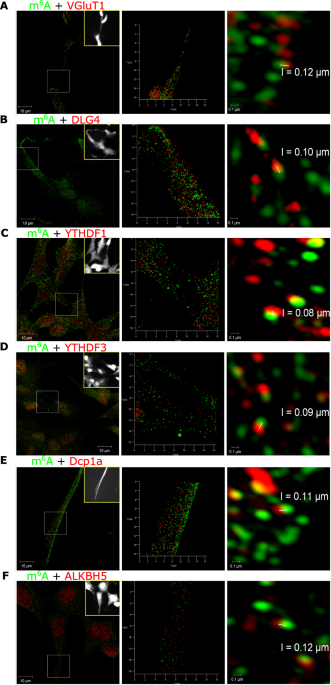
Modifying the m6A brain methylome by ALKBH5-mediated demethylation

Sensory neuron–derived NaV1.7 contributes to dorsal horn neuron
gad1a- FISH — Zebrafish UCL
Fluorescent ISH — Zebrafish UCL
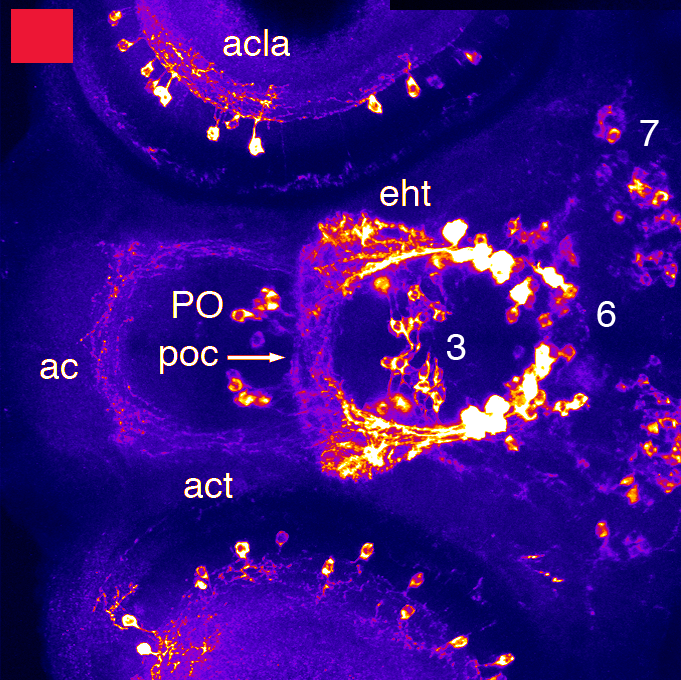
Neurotransmitters — Neurotransmitters — Zebrafish UCL

Full article: Potential of Müller Glia for Retina Neuroprotection
Recommandé pour vous
 Glutamate monosodique E62114 Jul 2023
Glutamate monosodique E62114 Jul 2023 Glutamate - Paris Store14 Jul 2023
Glutamate - Paris Store14 Jul 2023 Glutamate-Glutamine cycle Astrocyte in glutamate-glutamine metabolism14 Jul 2023
Glutamate-Glutamine cycle Astrocyte in glutamate-glutamine metabolism14 Jul 2023 Chemical structure of glutamate14 Jul 2023
Chemical structure of glutamate14 Jul 2023 Ajinomoto Ajinomoto AJI-NO-MOTO Glutamate de Sodium 1 kg : : Epicerie14 Jul 2023
Ajinomoto Ajinomoto AJI-NO-MOTO Glutamate de Sodium 1 kg : : Epicerie14 Jul 2023 Glutamate : 5 520 images, photos de stock, objets 3D et images vectorielles14 Jul 2023
Glutamate : 5 520 images, photos de stock, objets 3D et images vectorielles14 Jul 2023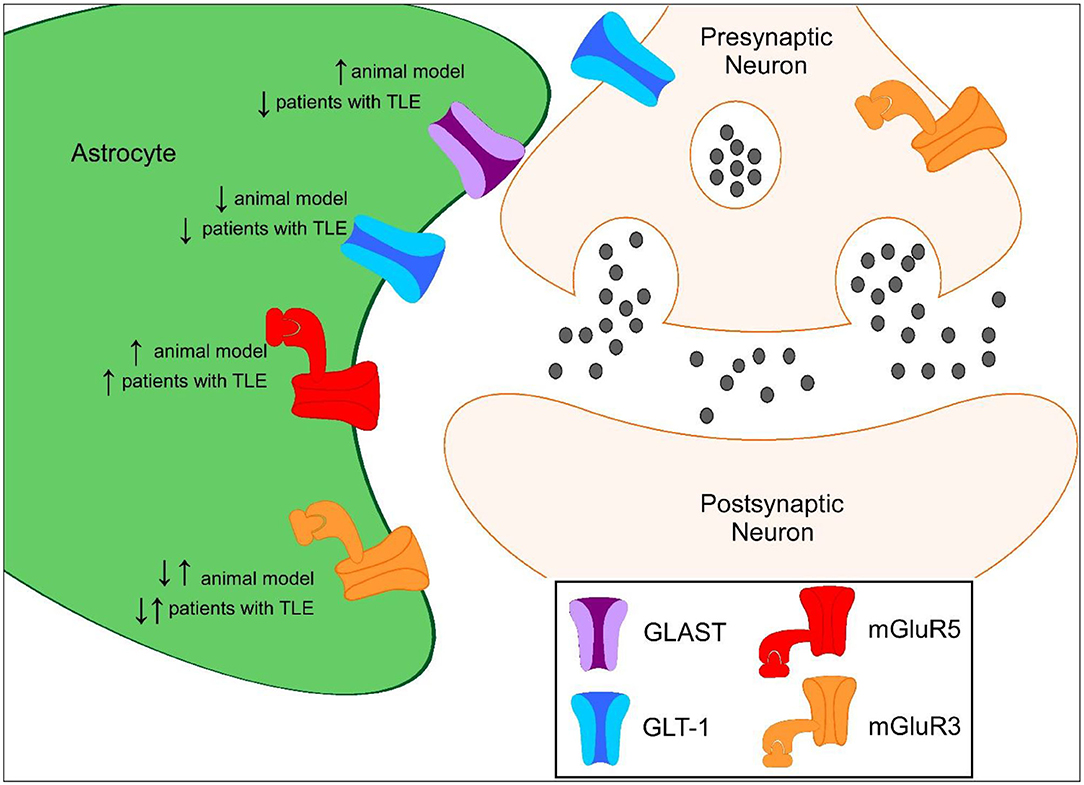 Frontiers Astrocyte Glutamate Uptake and Signaling as Novel Targets for Antiepileptogenic Therapy14 Jul 2023
Frontiers Astrocyte Glutamate Uptake and Signaling as Novel Targets for Antiepileptogenic Therapy14 Jul 2023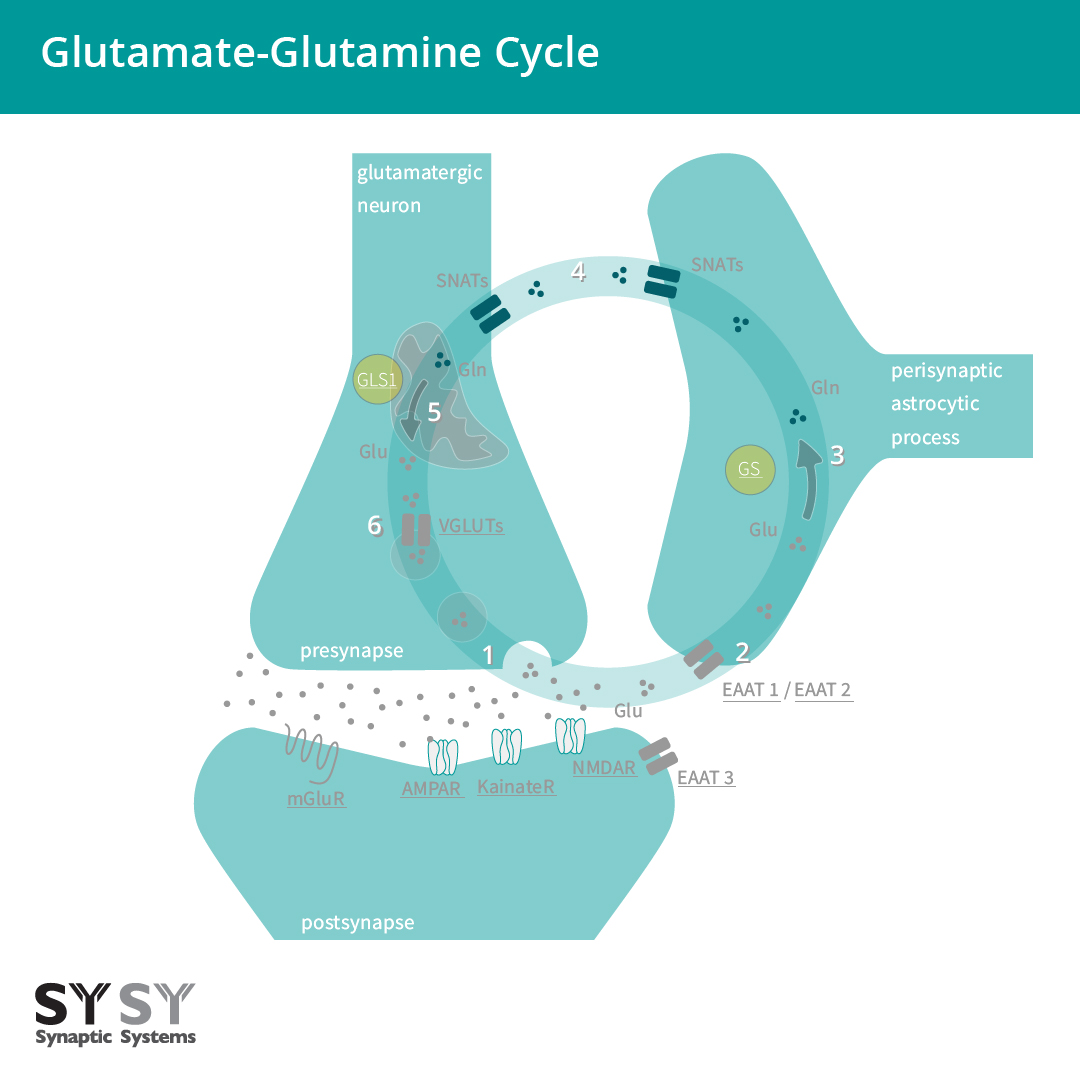 The Glutamatergic Synapse14 Jul 2023
The Glutamatergic Synapse14 Jul 2023 How do synaptic vesicles accumulate glutamate? – Kompass des Forschungsbereichs Information14 Jul 2023
How do synaptic vesicles accumulate glutamate? – Kompass des Forschungsbereichs Information14 Jul 2023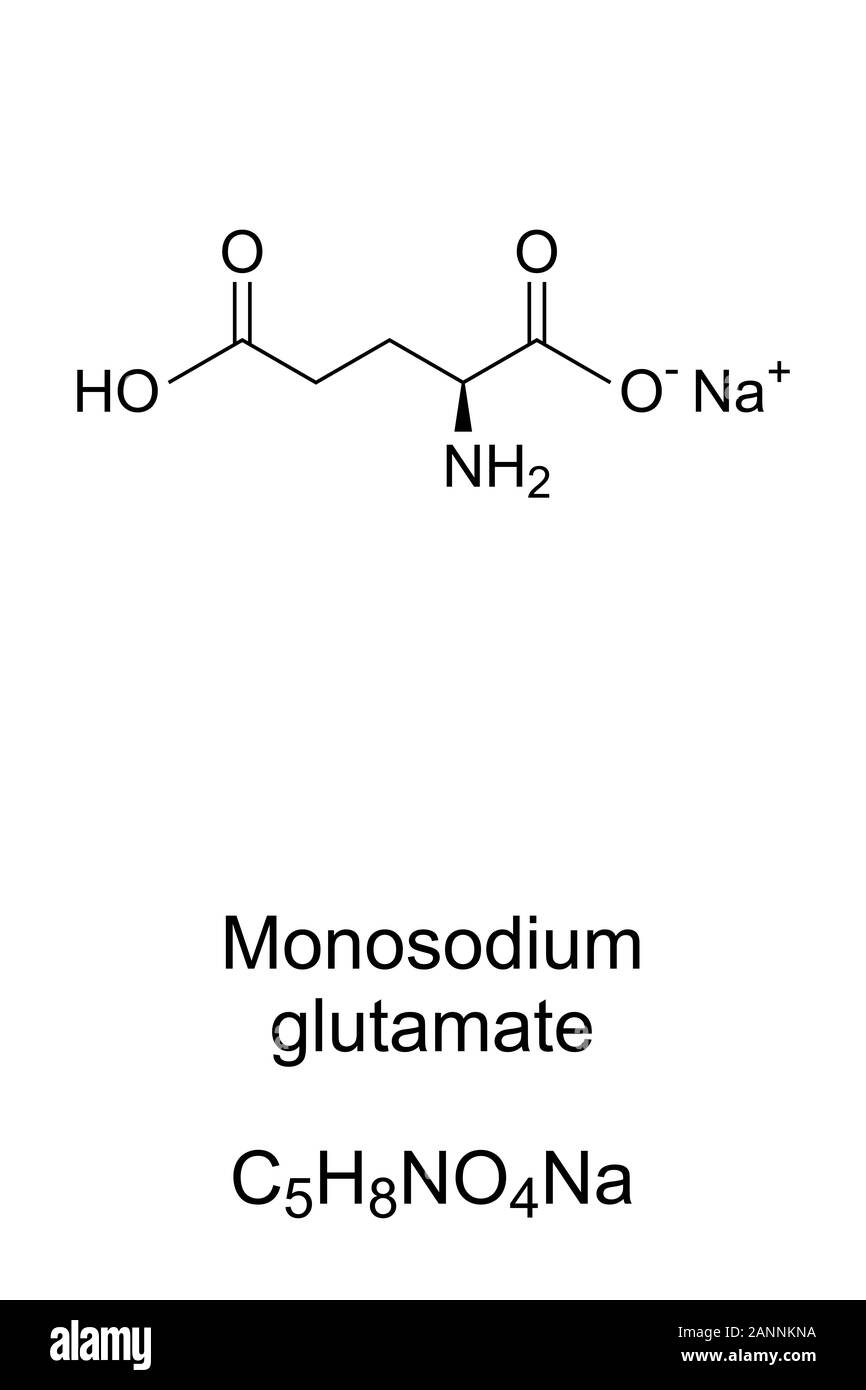 Chemistry chemical formula glutamate Banque d'images détourées - Alamy14 Jul 2023
Chemistry chemical formula glutamate Banque d'images détourées - Alamy14 Jul 2023
Tu pourrais aussi aimer
 jusqu'à 44% Deux packs de cartouches d'encre Canon 540XL/541XL14 Jul 2023
jusqu'à 44% Deux packs de cartouches d'encre Canon 540XL/541XL14 Jul 2023 La Vie en Rose - Southcentre Mall14 Jul 2023
La Vie en Rose - Southcentre Mall14 Jul 2023 (1 Pack) SanDisk 256GB MicroSD Nintendo Switch Micro SDXC Memory Card for Switch & Switch Lite SDSQXAO-256G Bundle with (1) GoRAM Plastic Case14 Jul 2023
(1 Pack) SanDisk 256GB MicroSD Nintendo Switch Micro SDXC Memory Card for Switch & Switch Lite SDSQXAO-256G Bundle with (1) GoRAM Plastic Case14 Jul 2023 Croquettes pour chiens14 Jul 2023
Croquettes pour chiens14 Jul 2023 Loquet De Porte Moustiquaire Pour Camping-car, Ensemble De Loquets De Porte De Camping-car, Poignée Droite, Installation Simple, Robuste Et Pratique, Ensemble De Loquets De Porte De Camping-car En ABS14 Jul 2023
Loquet De Porte Moustiquaire Pour Camping-car, Ensemble De Loquets De Porte De Camping-car, Poignée Droite, Installation Simple, Robuste Et Pratique, Ensemble De Loquets De Porte De Camping-car En ABS14 Jul 2023 Lampe de camping à 30 LED, lampe de travail de garage mains libres pour auto, garage, urgences, atelier avec support de réglage, crochet de suspension et base d'aimant - Chine Lampe LED14 Jul 2023
Lampe de camping à 30 LED, lampe de travail de garage mains libres pour auto, garage, urgences, atelier avec support de réglage, crochet de suspension et base d'aimant - Chine Lampe LED14 Jul 2023 CORRECTION - EFFACEUR - BLANCO14 Jul 2023
CORRECTION - EFFACEUR - BLANCO14 Jul 2023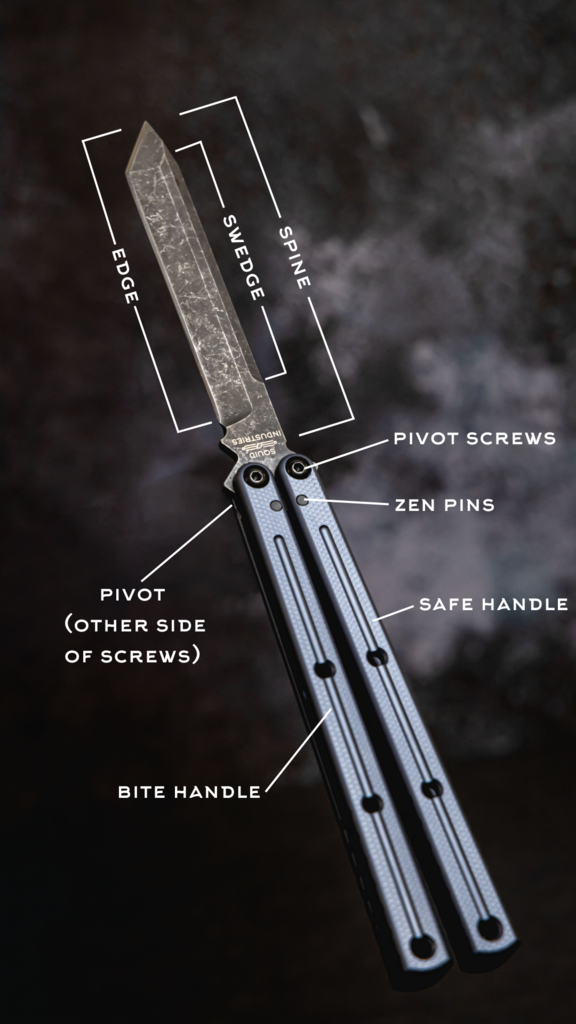 How to Butterfly Knife/Balisong for First-timers – Squid Industries14 Jul 2023
How to Butterfly Knife/Balisong for First-timers – Squid Industries14 Jul 2023/tapis-de-bain-modele-kawaii-sans-couture-avec-des-bonbons-et-des-bonbons-trucs-fous-en-style-cartoon.jpg.jpg) Tapis de bain Modèle kawaii sans couture avec des bonbons et des bonbons. trucs fous en style cartoon14 Jul 2023
Tapis de bain Modèle kawaii sans couture avec des bonbons et des bonbons. trucs fous en style cartoon14 Jul 2023 Beginner's guide to 18650 battery with easy-to-understand illustration - SkyGenius Online14 Jul 2023
Beginner's guide to 18650 battery with easy-to-understand illustration - SkyGenius Online14 Jul 2023